Geography and Landforms:
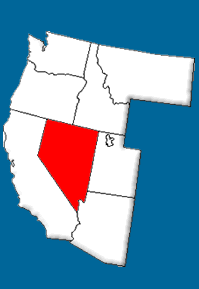
Most of the state of Nevada lies within the Great Basin, a large desert area that extends into Utah, California, Oregon, Wyoming, and Idaho. The land is broken up by more than 30 mountain ranges that extend from north to south throughout the state. At the western edge of the Basin, the Sierra Nevada, a rugged mountain range, forms part of the state's border with California. Lake Tahoe and several other spectacular mountain lakes in the Sierra Nevada are popular vacation spots.
|
 History:
Spanish explorers were probably the first white men to come to the Nevada region. They may have entered the southern portion of the area during the 1770s while journeying from New Mexico to California. But the Spanish did not establish any settlements in Nevada.
|
 Economy:
Most of Nevada's economic riches are located deep within the ground. The state is a leading producer of gold, silver, and mercury. Copper is still mined, although it is no longer as dominant as it was in the past.
|
 First Inhabitants:
Native Americans inhabited the region that is now the state of Nevada thousands of years before Spanish explorers and fur traders began to explore the area. Archaeological discoveries of bones and ashes in the southern portion of the state reveal that Native peoples lived there more than 20,000 years ago. Cave drawings left by these ancient people can be found in the Valley of Fire State Park near present-day Las Vegas.
|
Books Related To NevadaBad Kitty - Michele Jaffe The Case of the Deadly Desperados - Caroline Lawrence Death Mountain - Sherry Shahan Dragon's Gate - Laurence Yep Moon Shadow - Chris Platt Perfect - Ellen Hopkins S is for Silver: A Nevada Alphabet - Eleanor Coerr |
Famous Citizens:
|
| Capital: | Carson City |
| Entered Union: | October 31, 1864 |
| Population: | 2,839,099 |
| Area | 110,561 |
| Bird | Mountain Bluebird |
| Flower | Sagebrush |
| Nickname: | Silver State, Sage State, Sagebrush State |
| Governor | Brian Sandoval |
Places to Visit in Nevada: (Click the links to learn more.)
|