Geography and Landforms:
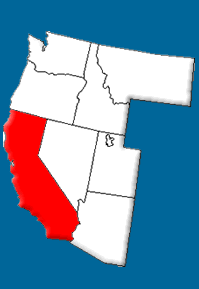
California has a diverse landscape made up of many unique geographic areas including the rocky Coastal Ranges, the Central Valley, the Klamath Mountains, the Transverse Range, the Cascades, the Sierra Nevada, and the Great Basin.
|
 History:
Juan Rodriquez Cabrillo was the first European to see the coast of
what is now California. He was a Portuguese explorer hired by the Spanish to lead an expedition in search of a passage connecting the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. Instead, he discovered San Diego Bay in 1542.
|
 Economy:
California is the nation's leading agricultural state, producing a wide variety of fruits and vegetables including carrots, lettuce, tomatoes, onions, and broccoli. The state's most valuable crops include cotton, grapes, and oranges. California is also a leader in the production of dairy products and wine.
|
 First Inhabitants:
California's earliest inhabitants were Asians who traveled the Bering Strait into North America using a now-vanished land bridge. More than 10,000 years ago, they settled throughout the region's diverse geographic areas and climates. Deserts and high mountains helped to separate these groups, and they lived peacefully in relative isolation from one another. Over many years, distinctive differences in lifestyle and culture developed among these groups, which included the Hupa, the Maidu, the Pomo, the Modic, and the Mohave tribes. More than 135 language dialects emerged.
|
Books Related To CaliforniaThe Ballad of Lucy Whipple - Karen Cushman The Bracelet - Yoshiko Uchida Buster Changes His Luck - Marc Brown By the Great Horn Spoon - Sid Fleischman A Day's Work - Eve Bunting Earthquake at Dawn - Kristiana Gregory Frida Maria: A Story of the Old Southwest - Deborah Lattimore G is for Golden: A California Alphabet - David Domeniconi Little Mama Forgets - Melanie Kroupa Parrot in the Oven: Mi Vida - Victor Martinez Quake!: Disaster in San Francisco - Gail Karwoski Snowshoe Thompson - Nancy Smiler Levinson The Trouble with Cats - Martha Freeman |
Famous Citizens:
|
| Capital: | Sacramento |
| Entered Union: | September 9, 1850 |
| Population: | 38,802,500 |
| Area | 163,696 |
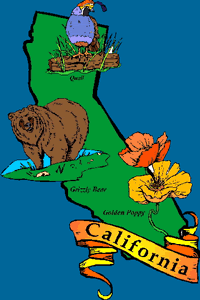
| Bird | California Valley Quail |
| Flower | California Poppy |
| Nickname: | The Golden State |
| Governor | Jerry Brown |
Places to Visit in California: (Click the links to learn more.)
|